Table of Contents
Introduction
Setting SMART goals is essential for HR managers to make a meaningful impact on their organizations.
However, 67% of HRs fail to set SMART goals and end up facing a certain set of challenges such as:
Lack of clarity
Unrealistic goals
Poor time management
No task prioritization
Decreased productivity
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of SMART goals in HR management.
By understanding the key principles and strategies behind SMART goals, HR managers can effectively align their objectives, track progress, and achieve tangible results.
Let’s dive in:
Understanding SMART Goals
SMART goals are a powerful framework that HR managers can use to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives.
By adhering to these principles, HR professionals can enhance their effectiveness in driving organizational success.
Let’s explore the key components of SMART goals:
- Specific: Clearly define the objective and what needs to be accomplished.
- Measurable: Establish concrete metrics to track progress and evaluate success.
- Achievable: Set realistic and attainable goals aligning the available resources.
- Relevant: Ensure the goals align with the organization’s objectives and priorities.
- Time-bound: Set deadlines and establish timeframes for achieving the goals.
Benefits of SMART goals for HR managers:
- Better alignment of HR initiatives with organizational goals
- Enhanced focus and clarity in goal-setting
- Clear communication of expectations and objectives
- Improved motivation and accountability among HR teams
By adopting the SMART framework, HR managers can effectively navigate the complexities of their roles and drive meaningful impact within their organizations.
Tracking and Analyzing SMART Goals
1. Specific Goals
Setting specific goals provides a clear direction and focus for your efforts.
It lets HR teams effectively allocate resources, make informed decisions, and prioritize tasks to achieve desired outcomes.
Specific goals eliminate ambiguity and enable HR managers to communicate expectations clearly, fostering a shared understanding among team members.
2. Measurable Goals
Measuring progress and success is essential to SMART goals in HR management.
By establishing quantifiable metrics and indicators, you can track the progress of their initiatives and determine if they are on track to achieve the desired outcomes.
Measurable goals provide concrete data points, allowing for objective evaluation and adjustment of strategies and tactics.
Don’t know how to analyze SMART goals?
Workstatus can help you monitor and measure SMART goals with the help of its most advanced features, such as:
Real-time Dashboard: Get a centralized dashboard that displays the progress of individual and team goals, allowing HR managers to track the completion status of tasks, projects, and milestones.
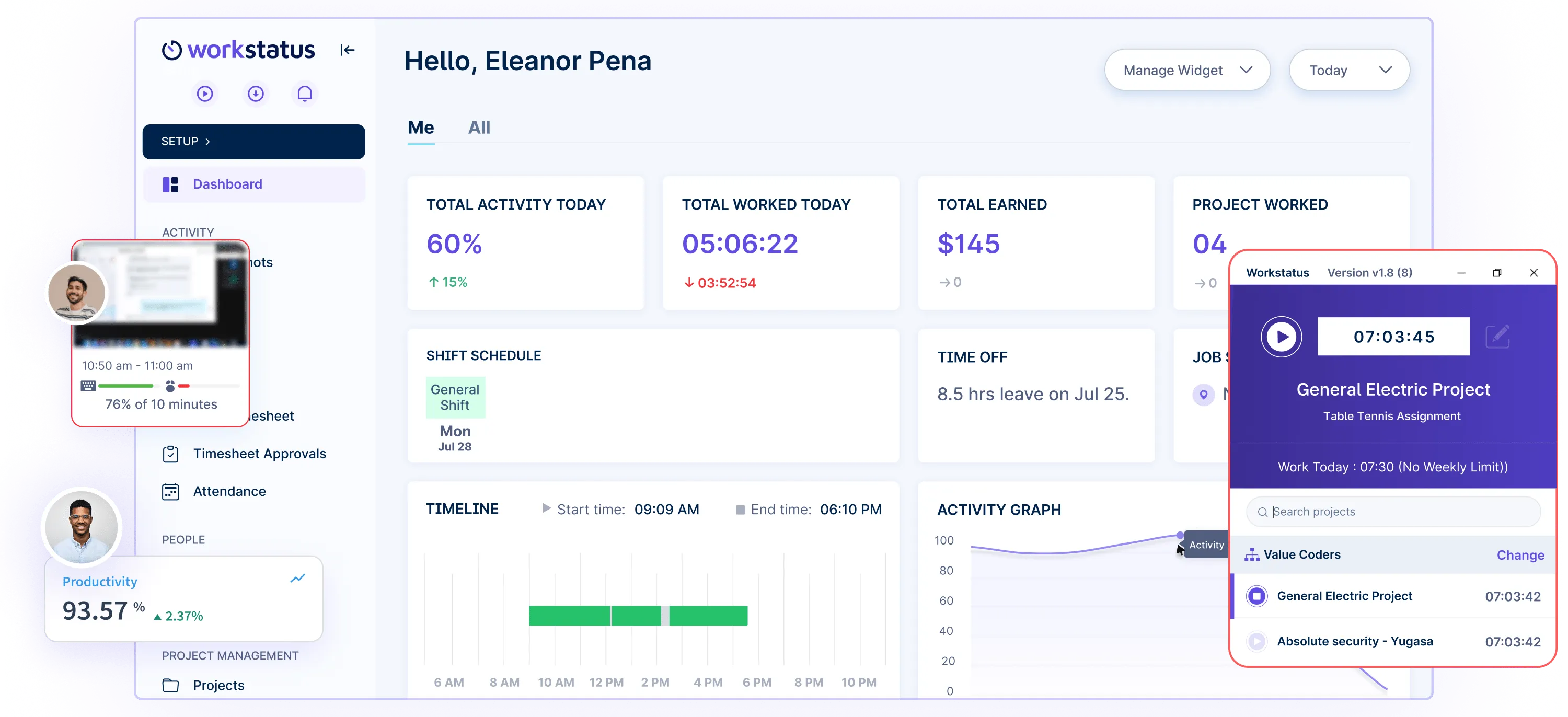
Visual Reports: Customizable reports and charts present data in a visually appealing manner. You can easily view and analyze metrics related to goal progress, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and communicate insights effectively.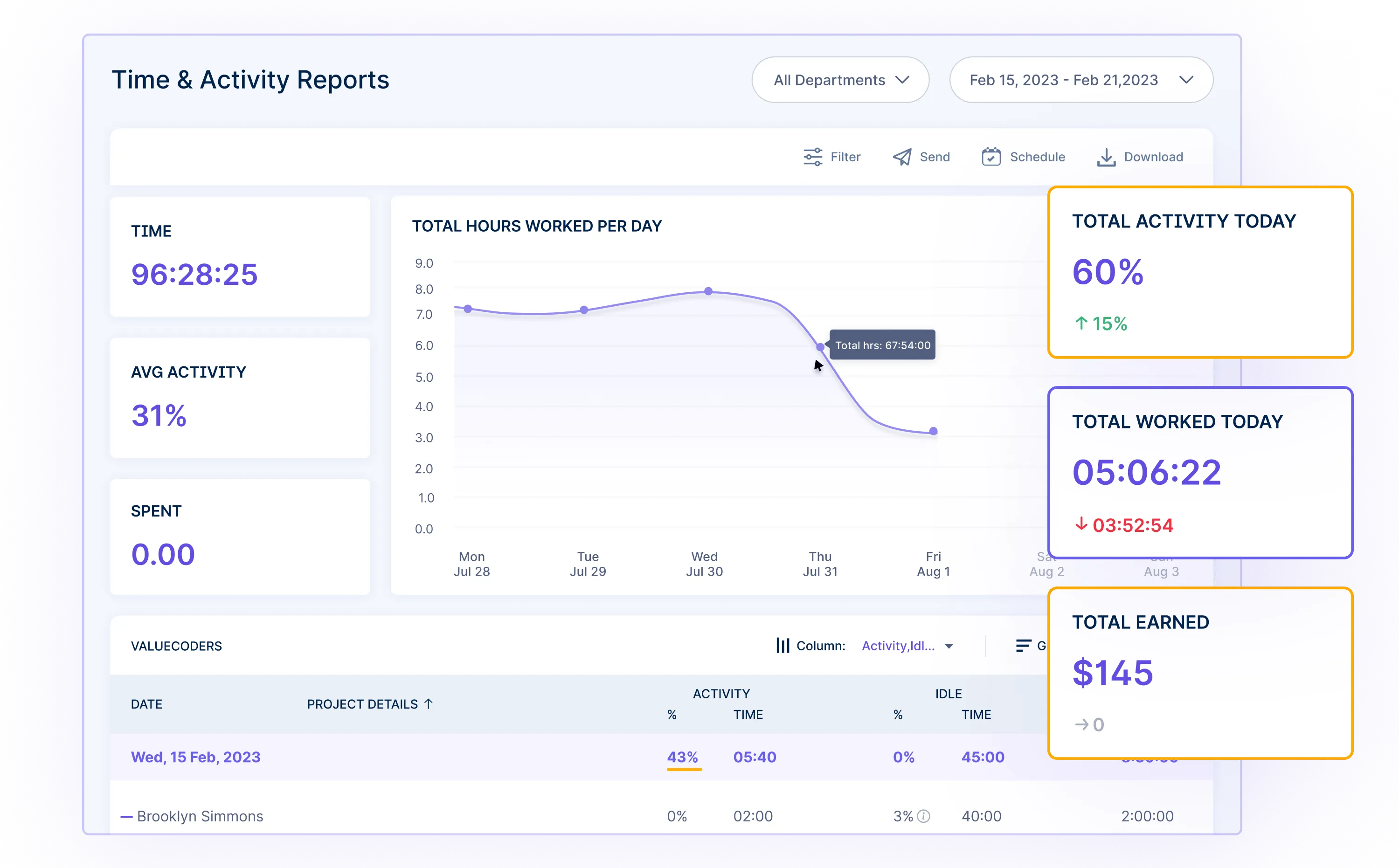 Task-level Metrics: HR managers can assign specific metrics to each task, such as completion percentage, time spent, or key performance indicators (KPIs). It enables them to measure progress objectively and identify areas for improvement.
Task-level Metrics: HR managers can assign specific metrics to each task, such as completion percentage, time spent, or key performance indicators (KPIs). It enables them to measure progress objectively and identify areas for improvement.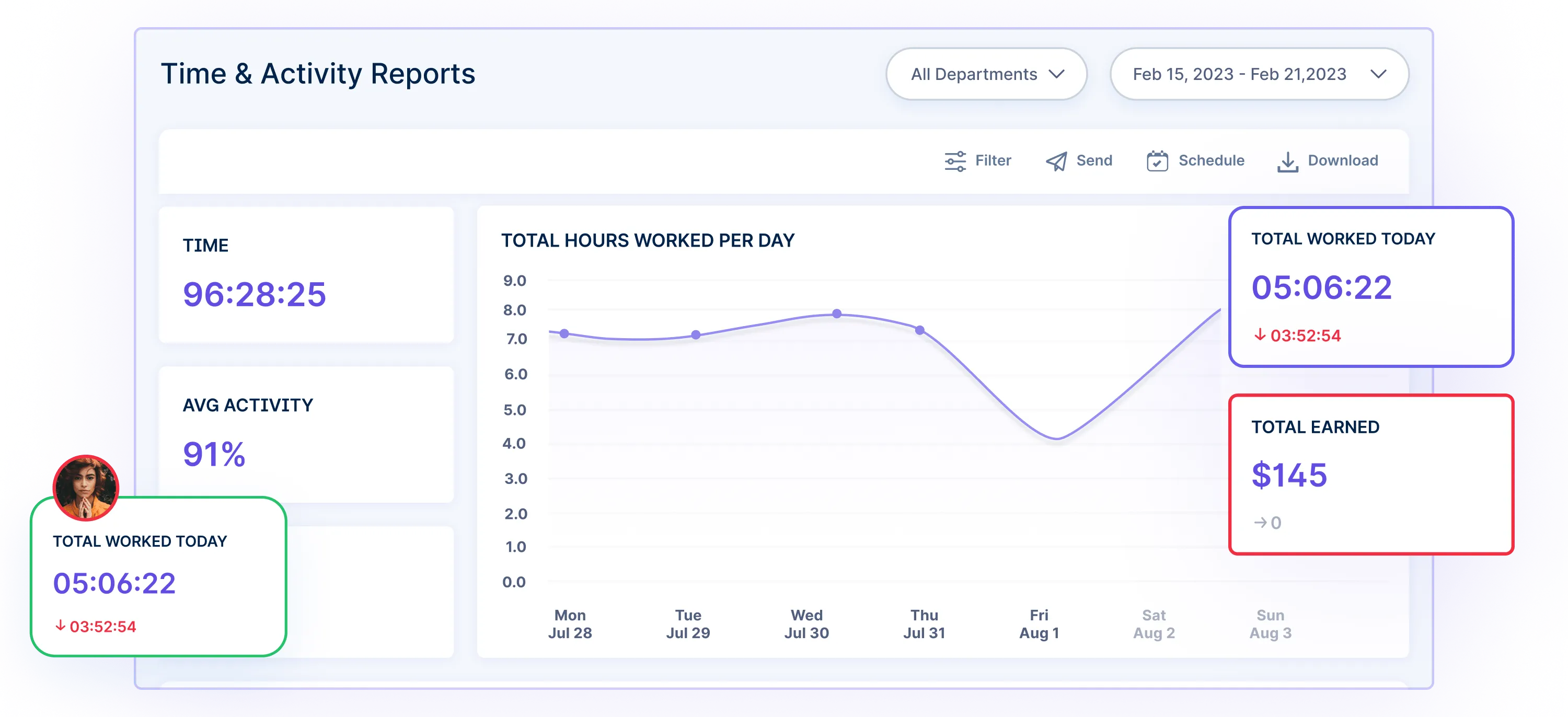 3. Achievable Goals
3. Achievable Goals
Setting achievable goals ensures that HR managers establish realistic targets that can be accomplished within the available:
- Resources
- Capabilities
- Constraints
It involves assessing the HR team’s skills and capacity, considering organizational factors, and breaking down larger goals into manageable tasks.
By setting achievable goals, you can maintain motivation, avoid burnout, and make steady progress toward long-term objectives.
4. Relevant Goals
Relevance is a key factor when setting SMART goals in HR management.
HR managers need to align their goals with the broader organizational objectives and the specific needs of the company, employees, and stakeholders.
HR managers can ensure that their efforts contribute meaningfully to the success of the organization by addressing challenges and driving positive outcomes for the workforce.
5. Time-bound Goals
Time-bound goals provide a sense of urgency and create a framework to plan and execute initiatives effectively.
By setting deadlines and establishing timeframes, HR managers can do the following:
- Avoid procrastination
- Prioritize tasks
- Allocate resources efficiently
Time-bound goals also facilitate timely adjustments and ensure that HR efforts stay on track toward achieving desired results.
Looking to track time-bound goals?
HR managers can use Workstatus to monitor their time-bound goals.
Here’s how Workstatus can help:
Project Deadlines: Set deadlines for individual projects within a goal. It helps manage time-bound goals by ensuring that tasks are completed within specified timeframes.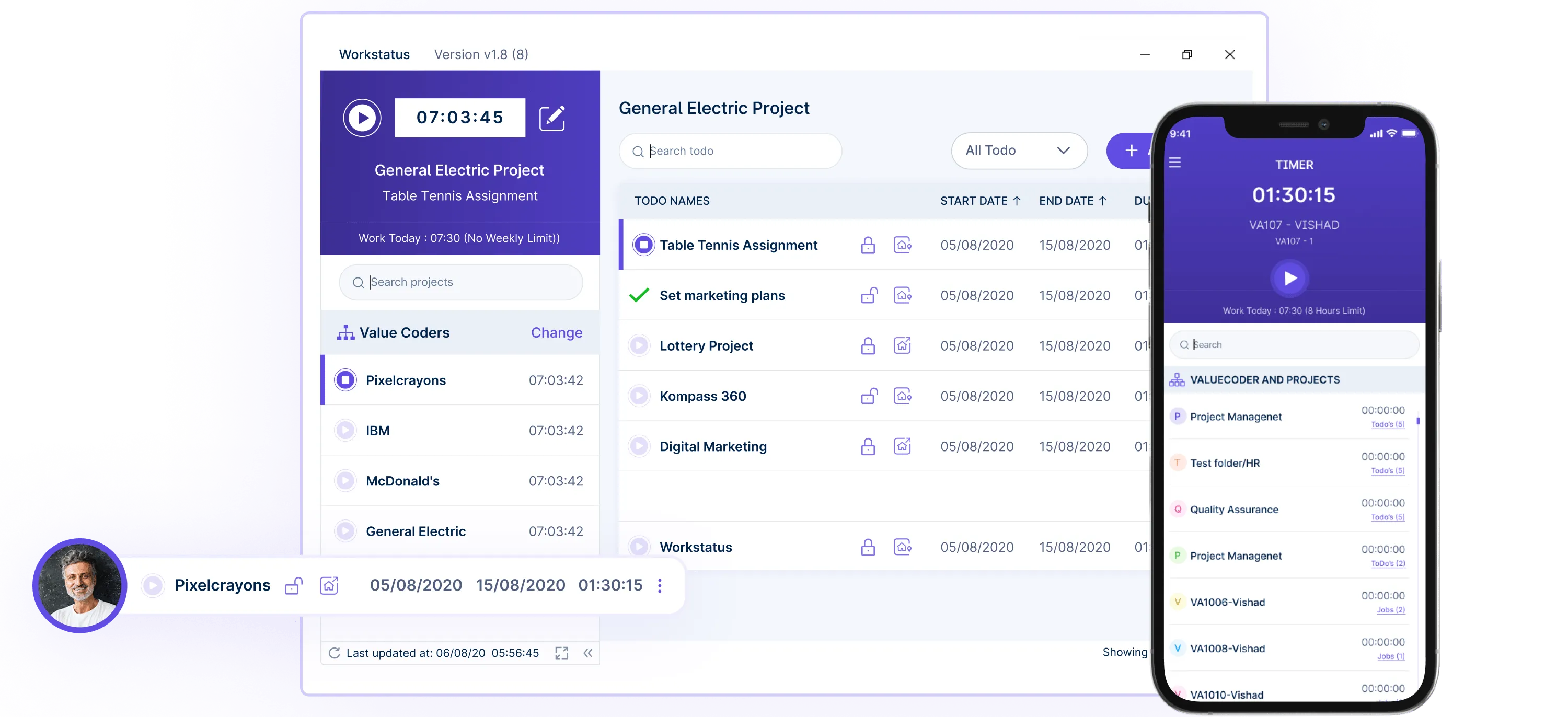 Timesheet Integration: Online timesheet management systems help seamlessly record and track the time spent on goal-related activities. It simplifies the process of time tracking and enhances accuracy.
Timesheet Integration: Online timesheet management systems help seamlessly record and track the time spent on goal-related activities. It simplifies the process of time tracking and enhances accuracy.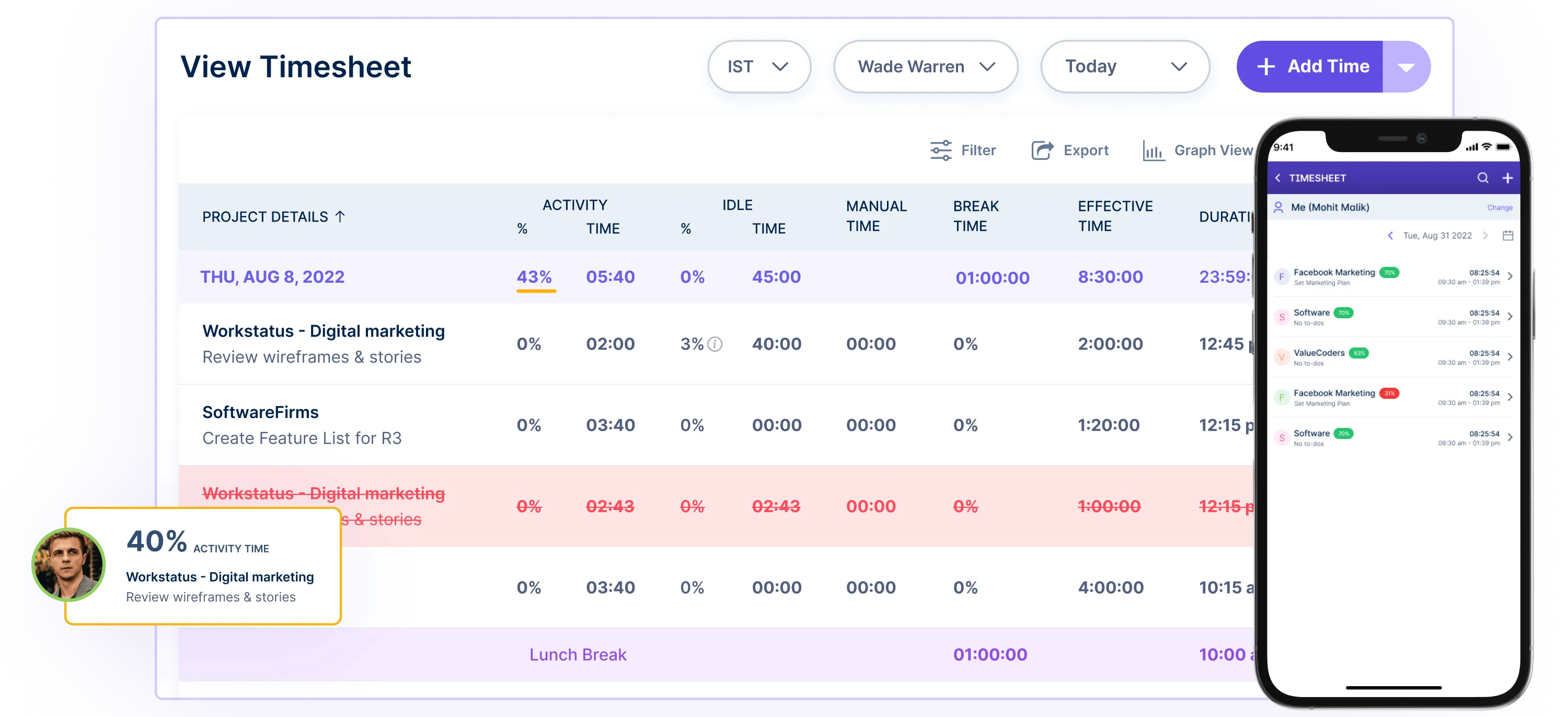
Capacity Planning: HR managers can assess team members’ availability and workload capacity, aiding in realistic goal setting. It ensures that time-bound goals are assigned appropriately, considering each team member’s capacity.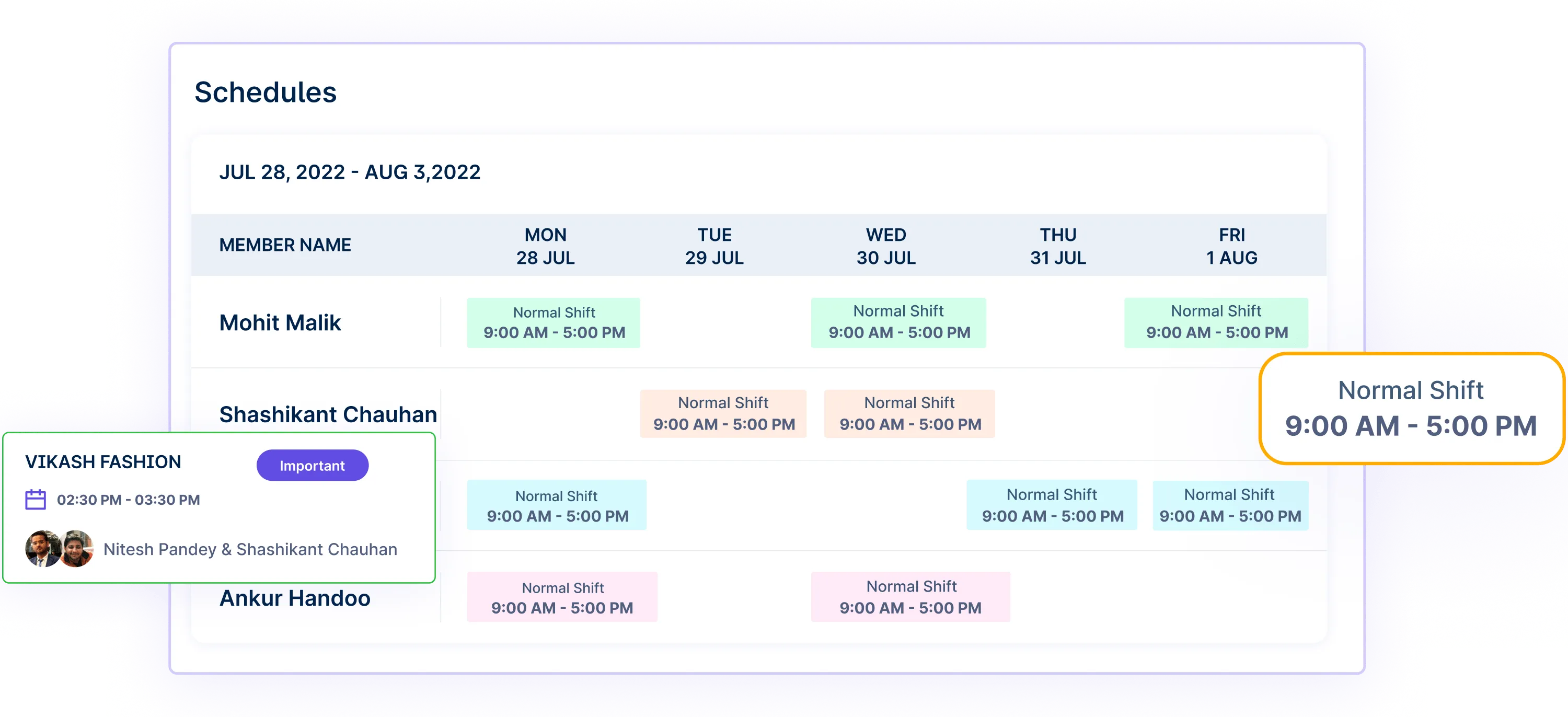
Implementing SMART Goals in HR Management
Here are some useful ways to integrate SMART goals with your existing HR system:
1. Assess Organizational Objectives
- Understand the organization’s mission, vision, and strategic priorities.
- Identify the key areas where HR can contribute and make a significant impact.
- Align HR goals with the broader organizational objectives to ensure relevance and strategic alignment
2. Establish Measurable Metrics
- Identify quantifiable indicators and metrics to track progress and success.
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with the specific goals.
- Use data and analytics to measure and evaluate the outcomes and impact of HR initiatives.
HR Manager Gayathri at Consulting firm, used Workstatus for goal tracking. She set specific goals for each department, assigned tasks to employees, and monitored progress in real-time. She was able to generate insightful reports, getting valuable insights into goal achievement. It improved her team’s performance by 23%.
3. Establish Time-bound Deadlines
- Set specific target dates and timeframes for achieving the goals
- Break down goals into milestones with intermediate deadlines to maintain focus and momentum.
- Regularly review progress and make necessary adjustments to stay on track.
4. Communicate and Cascade Goals
- Communicate the SMART goals to all relevant stakeholders, including HR teams, managers, and employees.
- Cascade the goals throughout the organization to ensure alignment and shared understanding.
- Foster a culture of ownership by involving everyone in the goal-setting process.
5. Regularly Monitor and Evaluate
- Continuously track progress against the defined metrics and milestones.
- Use progress reports, data analysis, and performance reviews to assess the effectiveness of HR initiatives.
- Identify areas of improvement and make necessary adjustments to ensure the goals are met successfully.
Ethical Considerations In HR Goal Setting
Ethical considerations in HR goal setting are not just a matter of compliance but also a reflection of the organization’s values and commitment to treating employees with respect and dignity.
Why Ethics Matter In HR Goal Setting?
-
Employee Well-Being
The ethical treatment of employees should be at the forefront of HR goal-setting.
Goals that promote a safe, inclusive, and supportive workplace contribute to the well-being of your workforce.
-
Organizational Reputation
Unethical HR practices can tarnish an organization’s reputation, making it less attractive to top talent and potential business partners.
A commitment to ethics can enhance your brand image.
-
Legal Compliance
Complying with labor laws and regulations is not just a legal requirement but also an ethical responsibility.
Ensuring that HR goals are aligned with legal standards is essential.
-
Equity and Inclusion
Ethical HR goals should address issues of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
A fair workplace that values differences fosters a culture of equality.
Ethical Challenges
Here, we will explore some common ethical challenges and strategies to address them:
1. Discrimination and Bias:
Unconscious bias in HR can lead to discriminatory practices and affect hiring, promotions, and employee development.
Solution: Implementing diversity training, creating standardized assessment criteria, and promoting inclusive hiring practices could be helpful to avoid bias.
2. Unrealistic Productivity Goals:
Setting unattainable productivity targets can lead to employee burnout and unethical behavior to meet goals.
Solution: Review and adjust goals regularly, considering employee feedback and workload capacity.
3. Privacy Violations:
Ethical concerns arise when HR goals involve intrusive monitoring or violate employee privacy.
Solution: Ensure that any data collection and monitoring practices are transparent, legal, and respectful of employees’ privacy rights.
4. Compensation Disparities:
Unequal pay or wage gaps can raise ethical concerns related to fairness and equity.
Solution: Conduct regular pay equity audits, address wage disparities, and ensure fair compensation practices.
5. Environmental and Social Responsibility:
Ethical HR goals should also consider an organization’s impact on the environment and society.
Solution: Integrate sustainability and corporate social responsibility goals into your HR strategy, promoting ethical behavior in all aspects of the organization.
By prioritizing ethics and fairness, HR managers can contribute to a positive workplace culture and the organization’s overall success.
International HR And Cross-Cultural SMART Goals
Challenges:
- Cultural Diversity: Different cultural norms and values can affect goal interpretation and achievement.
- Language Barriers: Language differences can impact goal clarity and specificity.
- Legal and Regulatory Variations: Complying with diverse labor laws adds complexity to HR goal setting.
- Time Zone Differences: Synchronizing activities and deadlines across time zones can be challenging.
Opportunities:
- Diverse Skill Sets: International teams offer a wide range of skills and experiences to leverage in SMART goals.
- Global Market Reach: HR goals can align with an organization’s global expansion strategies.
- Cultural Competency Development: SMART goals can promote cross-cultural understanding and collaboration.
Common Challenges in Achieving SMART Goals
Read the infographics to know the major challenges that companies face while executing SMART goals.

Workstatus can help you overcome these obstacles and optimize your performance for great success.
Monitoring and Adjusting Goals
Monitoring and adjusting goals is a vital process in achieving success.
By regularly tracking progress and making necessary adjustments, HR managers can ensure goals are on track and aligned with organizational objectives.
Here are key points to consider:
- Regular monitoring: Track goal progress in real-time to stay updated on performance.
- Data analysis: Analyze metrics and data to evaluate goal achievement and identify areas for improvement.
- Adjust timeframes: Assess if deadlines are realistic and make necessary adjustments to ensure achievability.
- Relevance check: Regularly review goals to ensure they align with changing organizational needs and priorities.
- Communication: Foster open communication to gather feedback and make collaborative adjustments.
- Embrace Agility: Be open to changes and adapt goals based on feedback and continuous improvement.
Regular monitoring and adjustment practices drive goal attainment, enhance performance, and contribute to organizational success.
Michael, an HR executive at a Marketing company, leveraged Workstatus to track employee productivity and ensure goal alignment. He identified potential bottlenecks, offered support where needed, and used productivity data to improve employee engagement by 19%.
How SMART HR Goals Benefit Employees
These goals offer numerous employee benefits that could result in a happier and more productive workforce.
Employee Development And Growth
SMART HR goals benefit by encouraging employee development and growth.
They are particular in nature, which means they clearly specify what staff are expected to do.
This level of clarity is essential since it helps employees better grasp their function within the organization.
When your company’s employees are aware of what is expected of them, they can put their efforts into developing the skills and knowledge needed to meet those expectations.
It promotes personal and professional development as employees strive to attain their objectives.
Increased Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is a critical component of employee well-being.
Setting SMART goals for team members not only helps employees understand the broad picture but also contributes to job happiness.
Furthermore, SMART goals are attainable and related to the jobs of the employees, assuring that they are progressing towards meaningful objectives that are consistent with the company’s vision and values.
This connection promotes a sense of purpose in their job and a positive work environment.
Improved Communication And Feedback
SMART goals also enhance successful workplace communication and feedback.
HR managers collaborate closely with employees to create these goals and establish success criteria.
This approach creates an open line for interaction between HR and staff members, allowing for clear expectations and the discussion of any potential barriers or challenges.
HR managers can provide guidance, support, and constructive feedback as needed to keep employees on track and improving.
This continuous feedback loop improves employee-manager connections, developing a culture of confidence and teamwork.
Closing Thoughts
SMART goals in HR management provide a strategic framework for success.
Combining SMART goals with Workstatus empowers HR managers to optimize productivity, goal monitoring, and performance evaluation.
HR managers can easily manage SMART goals, leading to improved performance, enhanced efficiency, and greater organizational success.