Table of Contents
Introduction
Businesses can save time, increase billing accuracy, and improve profits by tracking billable, non-billable, and total hours worked.
The idea is to maximize billable client hours while minimizing non-billable operational overhead. However, precise data is needed to identify the different types of hours.
Did You Know?
A research found that billable hours only constitute around 50-60% of total working hours.
Time tracking software automatically records hours with simple start/stop timers.
By assigning time entries to relevant billable projects or non-billable tasks, you can easily separate the billable hours vs. actual hours data.
This blog post explains the meaning of billable, non-billable, and total hours worked. It shows why you should automate tracking these hours and how to use Workstatus to track billable hours per employee.
Let’s learn more.
What Are Billable Hours?
Billable hours mean the time you work on a project for a client for which you can charge money. Many businesses, agencies, freelancers, and people who work for themselves use billable hours to make clients pay for their services.
The good thing about charging clients for the time you work is that it shows them exactly how you spent your time and why it’s worth the money they paid.
Your client may ask you to explain what you are billing them for. This will give them more clarity, and while it is extra work for you, it will show the client what you did and your progress.
Here are some situations when you will need to track the hours you can bill:
- Estimating costs for projects
- Sending invoices to clients
- Planning budgets for future projects
- Paying employees and freelancers
Depending on your agreement with the client and your company’s rules, you may or may not need to report billable hours on a timesheet. However, timesheets make it easy to track billable hours and ensure your estimates are accurate.
Real-Life Examples Of When Billable Hours Are Used For Employees?
Here are some examples of billable hours for you:
1) Consulting Firm
A consulting firm provides expert advice to businesses. They use billable hours to track how much time their employees spend working on each client’s project. The firm bills the client based on the hourly rate multiplied by the consultants’ billable hours. It ensures the client pays for the actual time and expertise provided.
Suppose a consulting firm has a team of consultants working on a project for a client. The client has agreed to pay $150 per hour for consulting services.
Total Hours Worked= 33 hours
Hourly Rate= $150
So, total Billable Amount= $150×33= $4,950
2) Law Firm
Lawyers use billable hours to keep track of the time they spend working on different cases for clients. The law firm bills the clients based on the lawyers’ hourly rates and the number of hours billed for that case. This allows the firm to charge clients fairly for the legal work done.
Consider a law firm handling a legal case for a client. The lawyer assigned to the case has an hourly rate of $250.
Total Hours Worked= 20 hours
Hourly Rate= $250
So, total Billable Amount= $250×20= $5,000
3) Freelancers
Freelance professionals like web developers, writers, or designers often bill their clients based on billable hours. They record the time spent on each project or task for a client. The freelancer then bills the client using their hourly rate multiplied by the billable hours worked. This way, the client pays for the actual work done.
Let’s say a freelance web developer is working on a website project for a client. The freelancer charges $75 per hour for their services.
Total Hours Worked= 30 hours
Hourly Rate= $75
So, total Billable Amount= $75×30= $2,250
Simplify Billable Hours Management with Workstatus
Workstatus is a tool that helps you easily track your time working on different tasks and projects.
Here’s how Workstatus can help you automate and simplify how you manage billable hours:
With Workstatus, you can start and stop a timer whenever you work, automatically recording your time on each thing you work on.
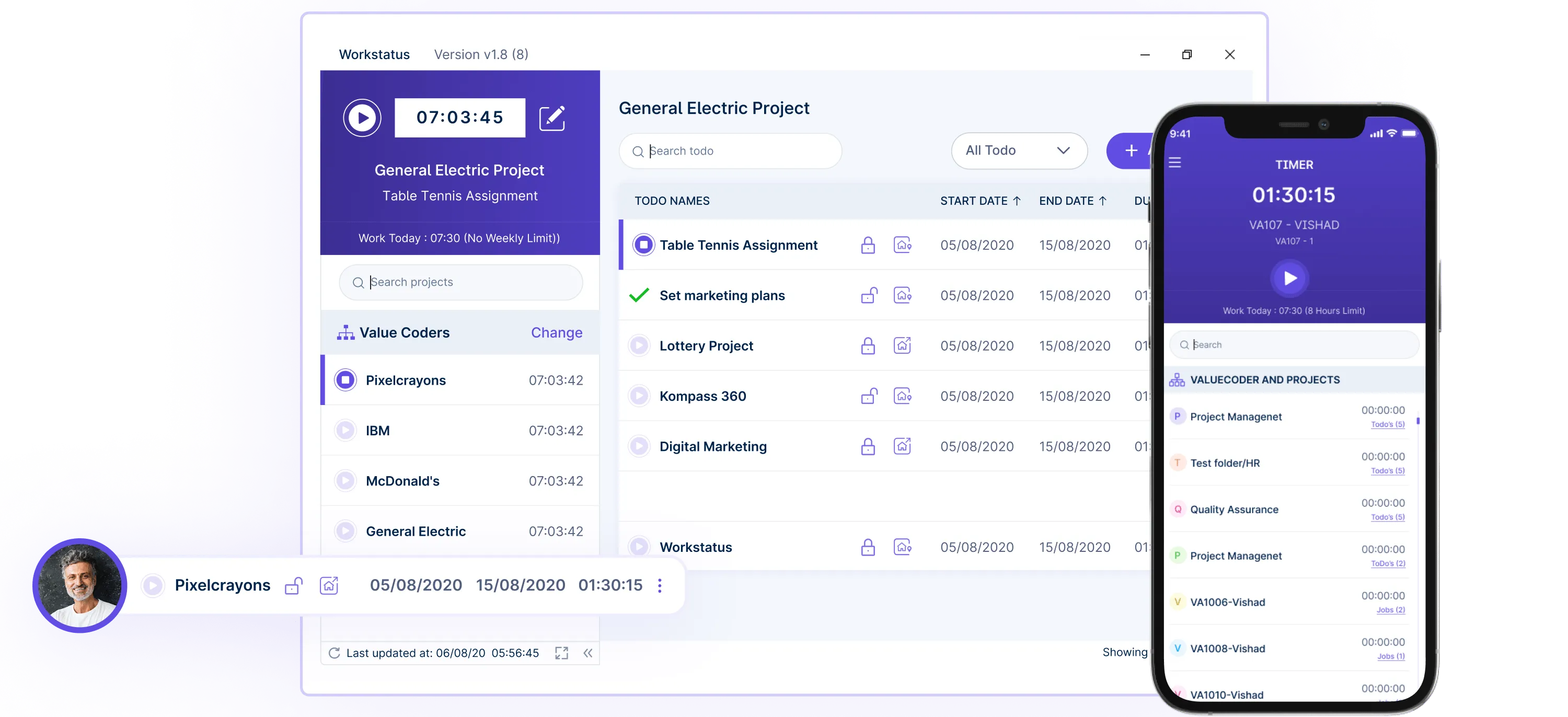
Workstatus then shows detailed reports about your time usage. You can see how many hours you worked on each project or task. The functionality makes it easy to understand where your time goes.
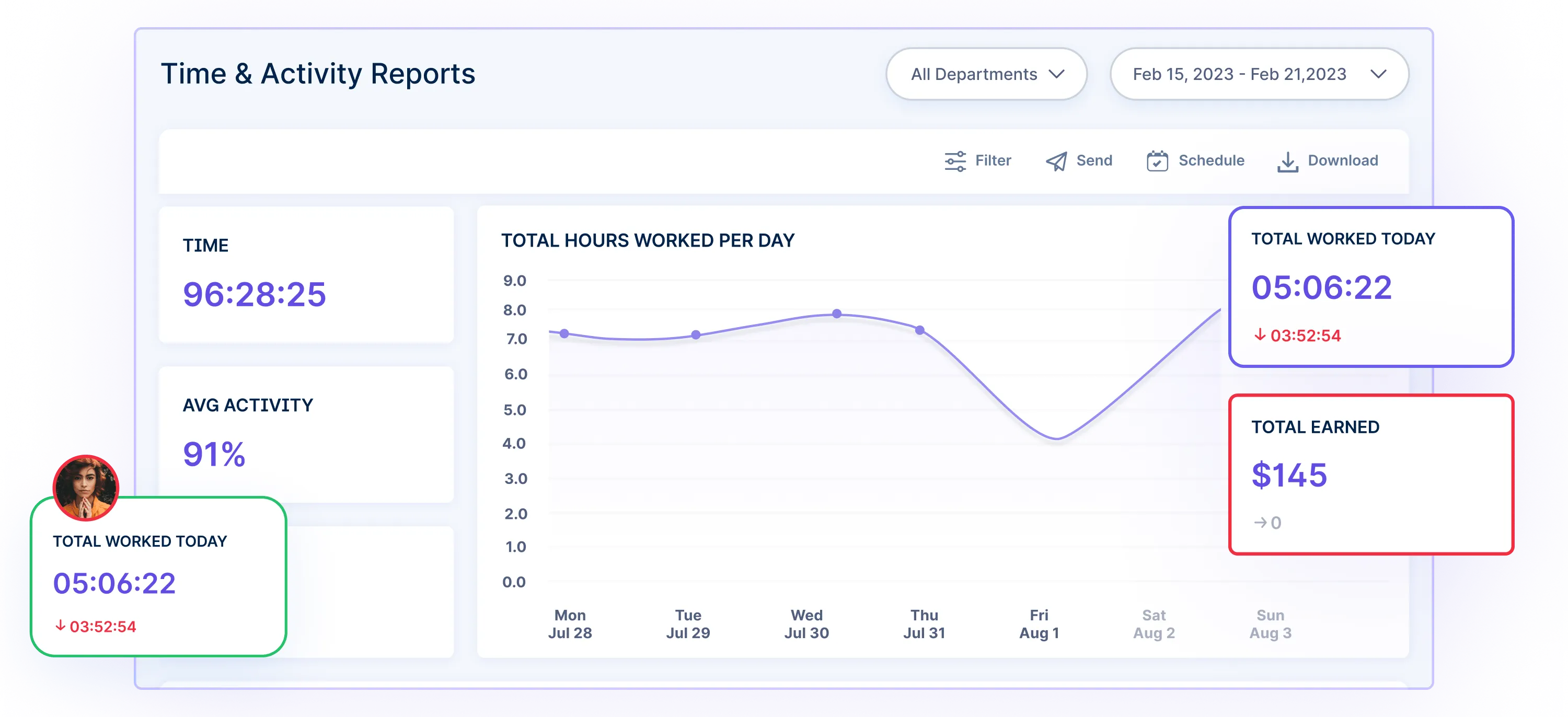
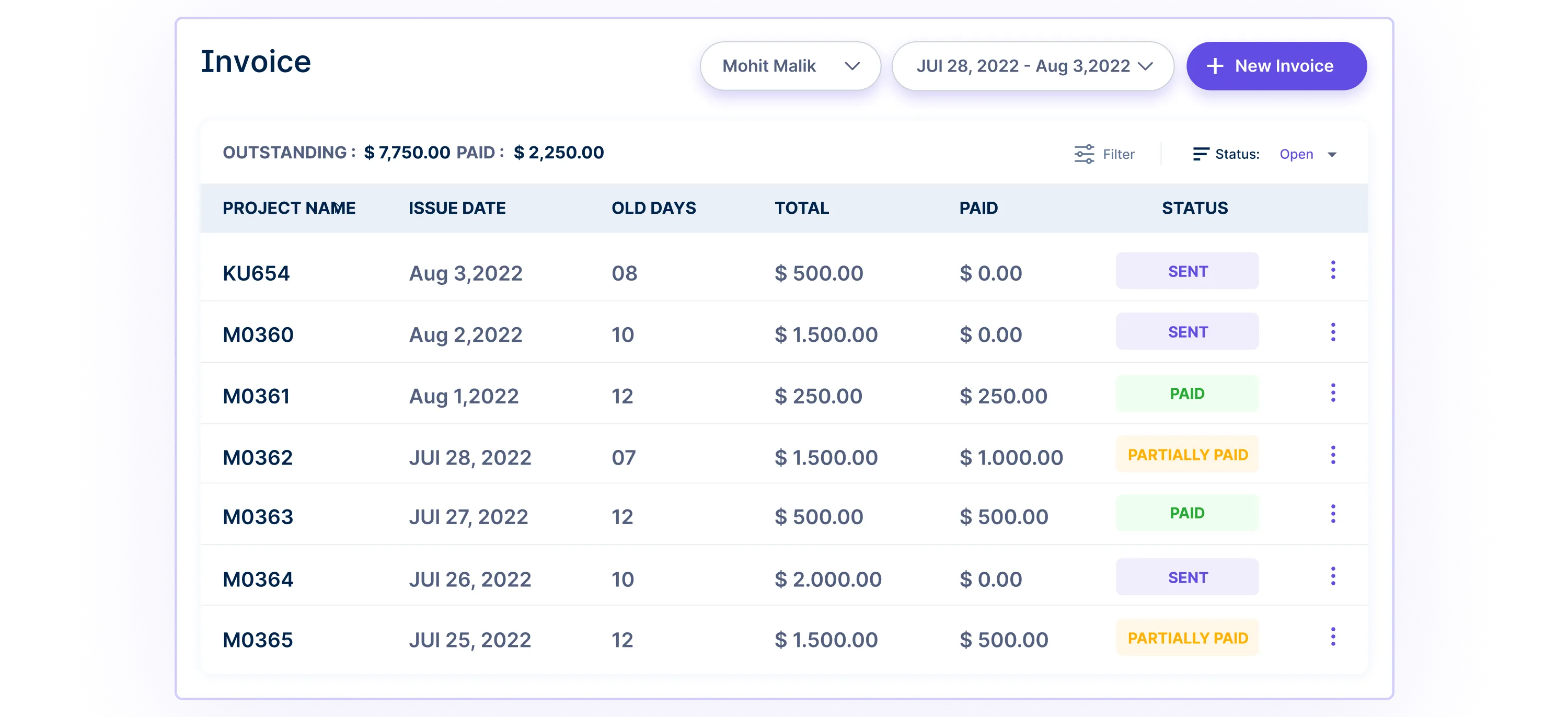
After tracking your time, Workstatus lets you quickly create client invoices based on your worked hours. It ensures you get paid accurately for all the work you’ve done.
If you work with a team, Workstatus also lets everyone see what each person is working on in real-time. This helps coordinate tasks and manage the team better.
Pros And Cons Of Billable Hours
If you are considering billable hours, you should consider this business model’s pros and cons. Here are the pros and cons of billable hours
Pros Of Billable Hours
1) Clarity Of Billing
One of the major advantages of using billable hours is the clarity and transparency it provides when billing clients. Clients know exactly how much they paid against what services.
2) Higher Flexibility
Being able to bill clients on an hour-by-hour basis provides tremendous flexibility for businesses. This allows them to quickly and easily adjust their work hours to meet the needs of their clients without needing to make larger changes to their overall schedule.
3) Incentivizes Efficiency
Billable hours incentivize professionals to work efficiently and quickly, as they are paid for the time they spend working on a project. This can lead to greater productivity and better quality work, as professionals are likely to put their best effort into projects when they know they will be compensated for it.
Cons Of Billable Hours:
1) Pressure To Bill More Hours
One downside to billing clients hourly is that some professionals may feel pressure to work more hours than they can work to get the desired amount paid. This can lead to fatigue and other health problems, as professionals work long hours without breaks.
2) Incomplete Or Inaccurate Records
If a professional cannot keep accurate records of their work hours, this can lead to billing complications. If a client disputes their bill, it may be difficult to prove that the professional worked the hours they claimed they did.
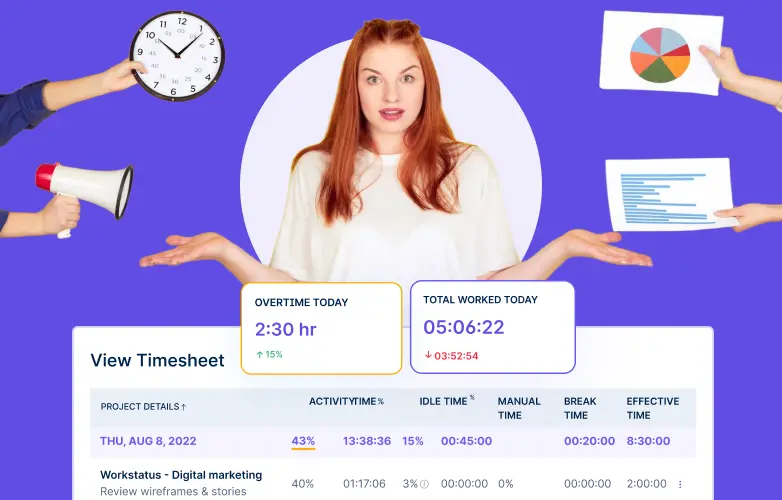
What Do You Mean By Non-Billable Hours For Employees?
What does non billable mean: Non-billable hours refer to the time employees spend on activities that cannot be charged or billed to clients or projects.
In simple terms, these are hours that the company or business cannot directly make money from.
Do you get paid for non-billable hours: Yes, employees are paid for total hours worked, non-billable hours are also important to track because they represent costs for the company or business. While these activities may be necessary for the organization’s operations and growth, they do not generate direct revenue.
Monitoring non-billable hours can help companies manage resources more efficiently and ensure employees spend appropriate time on billable (revenue-generating) work.
Real-Life Examples Of Non-Billable Hours
Let’s explore some real-life scenarios where non-billable hours come into play.
1) Administrative tasks: Time spent on internal meetings, training sessions, filing paperwork, or other administrative duties necessary for the business but not directly related to client work.
2) Professional development: Time spent on activities like attending conferences, taking courses, or learning new skills that improve the employee’s expertise but are not tied to a specific client project.
3) Vacation, sick leave, and personal time off: Hours when an employee is away from work and not actively working on any projects or tasks.
4) Business development: Time spent on marketing, networking, or pitching to potential new clients, which is essential for the company’s growth but not directly billable.
5) Internal projects: Hours spent on internal initiatives, system upgrades, or process improvements that benefit the company but are not client-facing.
Calculating Non-Billable Hours With Workstatus
Workstatus makes tracking and calculating your non-billable hours easy. When you start the Workstatus timer, you can label the task as “non-billable.” This separates it from the client project time that gets billed.
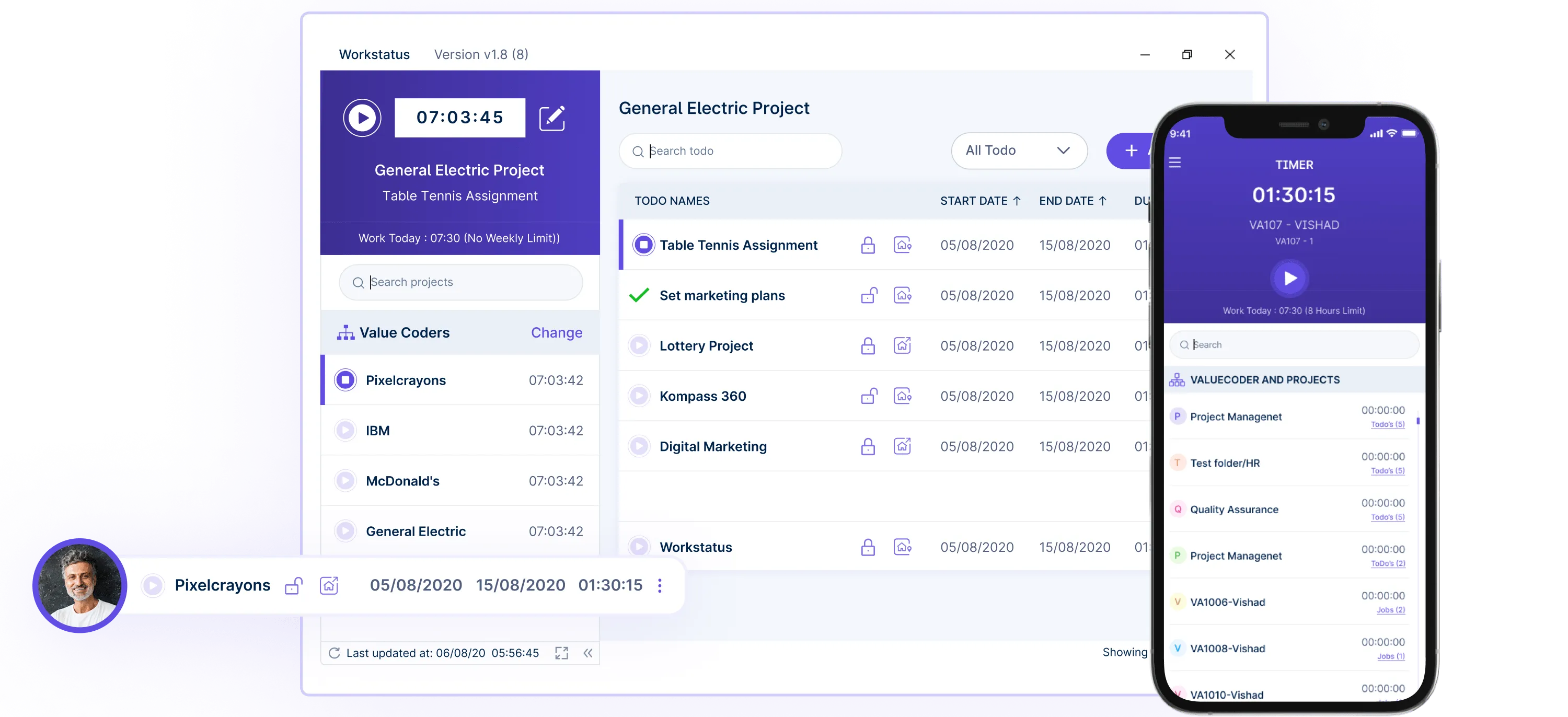
You could spend an hour having a team meeting every Monday morning. Just start the Workstatus timer labeled “team meeting,” and it will calculate that as non-billable time. The same goes for answering emails, watching training videos, or other internal tasks.
At the end of the week or month, your non-billable time reports show exactly how many hours you spent on administrative things versus client work.
It helps analyze your time usage and workflows. Are you spending too much time in meetings? Are certain non-billable tasks taking over?
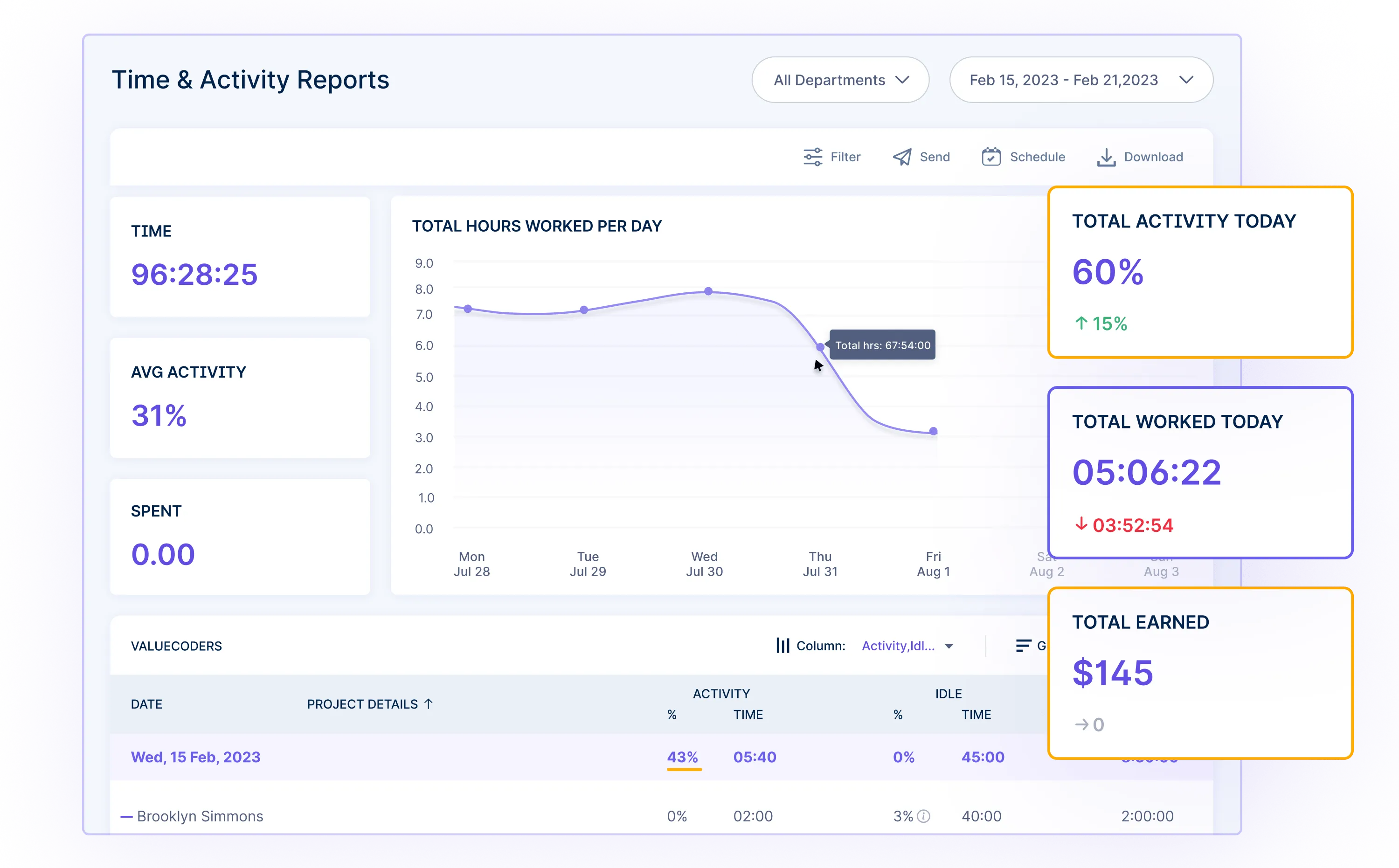
Tracking non-billable hours gives you a complete picture of where your time goes. With that information, you can identify areas for improvement and increase your billable utilization over time. It’s an important part of understanding your productivity at work.
Pros & Cons of Non-Billable Hours
The pros and cons of non-billable hours can help you decide on the number of non-billable hours for your employees. Here are some pros and cons.
Pros Of Non-Billable Hours:
1) Employee Development
Non-billable hours can be used to develop the skills and knowledge of employees. These activities include job training, attending conferences, or participating in team-building exercises that enhance employees’ professional development.
2) Reduced Stress Levels
Some employees find it less stressful when they do not have to track their hours or keep up with a busy work schedule. Non-billable hours can free up time to take care of personal matters, lowering stress levels.
3) Business Growth
Non-billable hours can be used for business development activities, such as networking and research, which can lead to long-term growth and success for the company and its employees.
Cons Of Non-Billable Hours:
1) Productivity Drops
When employees’ are working non-billable hours, they lack the motivation to deliver. That’s why you need to track productivity and time spent on non-billable hours as well. Because even though the employer is not billing the client, but still the employer is paying the employees; therefore, non-billable hours should contribute to long-term growth of the company.
2) Inability To Evaluate Employee Performance
When employees are not bringing in bucks for their time working, it can be difficult to accurately measure their performance. In some cases, employees might feel like they are not given the same level of appreciation as those who are paid by the hour, leading to a loss of morale.
What Do You Mean By Hours Worked?
Hours worked refers to all the time an employee spends performing duties and responsibilities.
It includes their regular scheduled hours, overtime hours, breaks, meetings, and training sessions—basically any time they spend at their workplace.
Companies track total hours worked each week or pay period. This determines how much an employee gets paid, including any overtime pay they earn. It also factors into calculating things like vacation time and other benefits.
While it may not all be physically working, any time an employee has to be at their job site counts as hours worked.
It’s the complete duration they are on the clock performing work activities and obligations.
Real-Life Examples Of When Hours Worked Are Used For Employees?
1) Overtime pay: Hours worked are used to calculate the amount of overtime pay an employee is entitled to. If an employee works more than 40 hours a week, they are typically entitled to time-and-a-half pay for those additional hours and extra pay for every eight hours worked beyond the 40-hour threshold.
2) Benefits Eligibility: Some companies have benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, that are based on the number of hours worked by an employee. Eligibility for these benefits is determined by the number of hours worked by an employee, so hours are often used when determining an employee’s eligibility for these benefits.
3) Attendance Tracking: Employers may use the number of hours employees work to track attendance and punctuality. This can be used to monitor employee productivity, identify patterns of absenteeism, and ensure that employees are working the hours for which they are being paid.
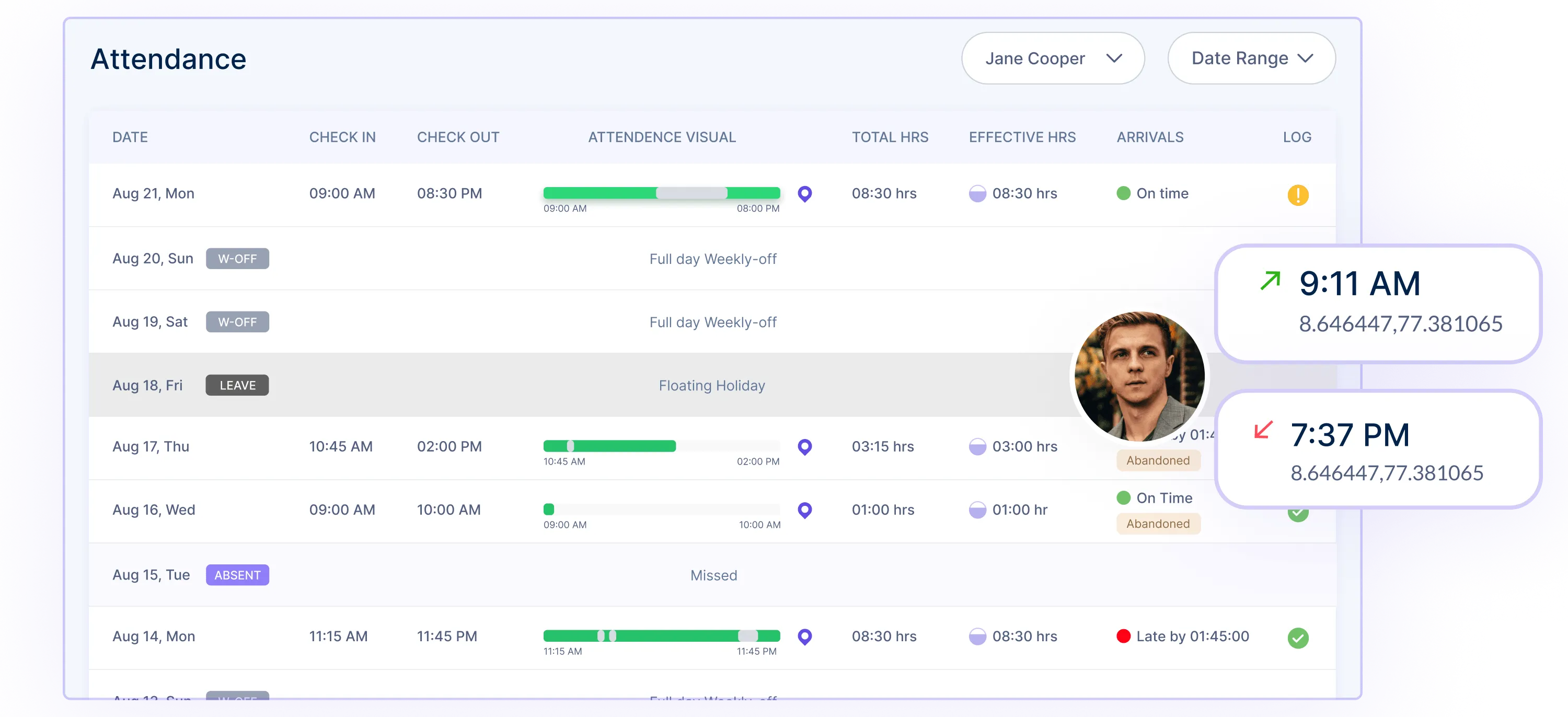
Pros & Cons of Hours Worked
There are pros and cons to hours worked concept. Some people work best under pressure, while others prefer more relaxed schedules. Here are some of the benefits and challenges to hours worked method of managing time and deciding payroll:
Pros Of Hours Worked:
1) Accurate Record-Keeping
By tracking the number of hours worked, employers can ensure that they pay employees for the exact amount of time they have worked.
2) Better Time Management
By tracking the number of hours worked, individuals and teams can better manage their time and ensure that they are using it effectively.
3) Accurate Billing
Tracking the number of hours worked can help ensure that clients are billed accurately for the time spent on their projects and can avoid misunderstandings or overcharges.
Cons Of Hours Worked:
1) Burnout Among Employees
When employees are constantly monitored and evaluated for their work hours, it can lead to burnout. This can decrease productivity and morale in the workplace.
2) Increased Turnover Rates
When hours are tightly regimented, employees may feel pressured to continuously work long hours to maintain their positions. This can lead to higher turnover rates among employees.
Comparison Table: Billable Hours vs. Non-Billable Hours vs. Hours Worked
Read the infographics below to get a complete overview of billable, non-billable, and hours worked.

Tips For Managing Billable Hours, Non-Billable Hours, And Hours Worked
Here are some billable hours best practices to manage your billable hours, non-billable hours, and hours worked:
1) Use a Time Tracking Tool
Apps like Workstatus make it easy to separate billable and non-billable time. You can quickly start/stop timers and add notes about what you’re working on.
2) Block Out Focus Time
Dedicate chunks of time with no meetings or distractions to grind through billable project work. This boosts productivity.
3) Schedule Non-Billable Tasks
Rather than scatter them throughout the day, put non-billable items like checking emails into scheduled time blocks.
4) Take Real Breaks
Don’t work through lunch or forgo breaks. It hurts motivation and focus. Use your break times as intended to recharge.
5) Review Time Data
Periodically analyze your time reports. Look for areas to cut non-billable time and maximize billable utilization.
Conclusion:
Don’t waste time manually tracking billable and non-billable hours. Using a tool like Workstatus automates the process for you.
With just a click, you can start a timer labelled for client billable work or internal non-billable tasks. Workstatus runs in the background, precisely recording your hours.
At the end of the week, it automatically calculates total billable vs non-billable time with accurate reporting. No guesswork and no billing mistakes. You can focus on productive priorities instead of administrative time tracking headaches.
Automating hour tracking means less busy work and more time for revenue-generating client projects that grow your business.
Let the software handle the administrative lifting to maximize your billable utilization.
Give Workstatus a try for a simplified time tracking experience.