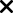Table of Contents
Introduction
Various considerations may cross your mind when contemplating extra hours at work.
One common concern is whether overtime comes with higher taxes and, more fundamentally, whether the additional effort is worthwhile.
Many individuals assume that working more hours and earning more money inevitably leads to a higher tax burden.
While this might seem logical, the reality is more nuanced. Working overtime doesn’t necessarily mean making less money due to increased taxes.
However, to avoid any unwelcome surprise, it’s essential to delve into the intricacies of overtime taxation. In this blog, we’ll provide comprehensive insights into:
- What qualifies as overtime, and what tax implications it brings?
- How is overtime pay calculated, and how does it affect overall earnings?
- The difference between federal and state taxes on overtime income.
- The role of tax brackets in determining overtime taxation.
Let’s get started.
What Constitutes Overtime Hours?
Overtime hours are hours worked beyond the standard or agreed-upon workweek.
Those additional hours usually qualify as overtime when an individual exceeds 40 weekly work hours.
These extra hours typically come with a higher pay rate, often 1.5 times the regular hourly wage, as mandated by labor laws.
Regular Pay Vs. Overtime Pay
There are two main categories in the realm of earnings, and both are subject to taxes.
- Regular Pay
- Overtime Pay
Regular pay is the standard compensation employees receive for a typical 40-hour workweek. It doesn’t encompass additional payments like overtime pay, bonuses, benefits, or reimbursements.
The regular rate of pay is calculated by the following method.
On the other hand, overtime pay comes into play when a non-exempt employee works more than 40 hours per week.
This extra compensation is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), ensuring that non-exempt employees receive at least the minimum wage and overtime pay at one and a half times their regular pay rate.
It’s important to note that regular and overtime pay are taxable forms of income.
Pro Tip:
An overtime tracker can significantly enhance your approach to regular and overtime pay.
Workstatus offers a streamlined Time Tracking feature that helps businesses accurately record hours worked, simplifying payroll processes and ensuring compliance with overtime regulations.

Different Types Of Overtime Pay Models
1. Time-and-a-Half
This standard overtime pay model compensates employees at 1.5 times their regular pay for each additional hour worked beyond the normal workweek.
For instance, if an employee’s regular hourly wage is $15, they would receive $22.50 per hour for overtime.
2. Double-Time
In this model, employees receive double their regular pay rate for overtime hours.
Using the same example, if an employee’s regular hourly wage is $15, they would be paid $30 per hour for each overtime hour.
3. Fixed Bonuses
Some industries opt for fixed bonuses as overtime compensation.
For instance, an employee might receive a set bonus amount for working beyond regular hours, regardless of the overtime hours. This could be a flat bonus of $100 for each overtime shift.
4. Compensatory Time Off
Employees may accrue extra paid time off for overtime hours instead of monetary compensation.
For example, employees who work 10 hours of overtime might be entitled to an additional 15 hours of paid time off to be taken later.
Importance Of Understanding Your Overtime Pay Policy
1. Financial Planning
Knowing how overtime is compensated helps in budgeting and financial planning.
2. Legal Compliance
Understanding overtime policies ensures compliance with labor laws and regulations compliance.
3. Employee Rights
Awareness of overtime policies empowers employees to assert their rights regarding fair compensation.
4. Avoiding Disputes
Clear knowledge of overtime policies minimizes the risk of disputes between employers and employees.
5. Maximizing Earnings
Being informed about overtime structures enables employees to maximize their earnings within legal boundaries.
Does overtime get taxed more?
No, overtime is not taxed more than regular pay. Your overall annual income and tax bracket determine your tax liability.
While working overtime might temporarily place you in a higher tax bracket for that specific pay period, it doesn’t result in higher taxes on all your income.
The marginal tax rate, representing the additional tax on each extra dollar earned, is the reason for this perception.
However, your annual taxes are calculated based on your overall earnings, ensuring fairness in taxation.
How is overtime taxed and its impact on your Income Tax
1. Higher Tax Bracket
Overtime can push you into a higher income tax bracket, resulting in a more significant percentage of your income being taxed.
2. Increased Tax Liability
Overtime earnings contribute to a higher taxable income, potentially leading to a higher overall tax liability at the end of the year.
3. Changes in Deductions
Overtime may affect your eligibility for certain deductions or credits, altering your overall tax situation.
4. Social Security and Medicare Taxes
Overtime can increase your contribution to Social Security and Medicare taxes, impacting your take-home pay.
5. Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) Impact
Overtime earnings may trigger the Alternative Minimum Tax, affecting the deductions and credits you can claim.
Variations In Overtime Taxation Across Different Countries
There are variations in overtime taxation across other countries compared to India. Some examples include:
1. United States
- Alabama: Full-time hourly waged employees are exempt from paying state income taxes on work performed more than 40 hours per week, starting from January 1, 2024
- New York and California: Overtime income is taxed at a higher rate in these high-tax states
- Florida, Tennessee, and Texas: These states do not impose any income taxes, so overtime pay is not taxed differently than regular pa
2. Canada
Overtime pay is generally taxed as ordinary income, with varying rates depending on the province and the individual’s tax bracket.
3. United Kingdom
Employees in the UK are entitled to a minimum of 28 days of paid annual leave, including bank and public holidays. Overtime pay is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to National Insurance contributions.
4. Australia
Employees in Australia are entitled to a maximum of 38 hours of overtime per year, with overtime pay rates typically calculated as 1.5 to 2 times the standard hourly rate. Overtime pay is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to the Medicare levy.
5. Japan
Employees in Japan are entitled to a maximum of 45 hours of overtime per year, with overtime pay rates typically calculated as 1.5 to 2 times the standard hourly rate.
Overtime pay is taxed as ordinary income and is subject to various social insurance contributions.
In India, overtime allowance is fully taxable in the hands of the employee and is not exempted under Section 10 of the Income Tax Act.
However, the tax rates and regulations may vary depending on the individual’s residential status and income.
How Is Overtime Tax Calculated?
1. USA
Overtime tax in the USA is calculated like regular income tax.
This means that your overtime earnings are added to your regular earnings, and your total income is taxed according to your tax bracket.
Here is an example of how to calculate overtime tax:
An employee earns $20 per hour and works 40 regular hours and 10 overtime hours weekly.
- Regular pay:
Regular hours * Regular pay rate = 40 hours * $20/hour = $800
- Overtime pay:
Overtime hours * Overtime pay rate = 10 hours * ($20/hour * 1.5) = $300
- Total pay:
Regular pay + Overtime pay = $800 + $300 = $1100
- Federal income tax withholding:
Total pay * Federal income tax rate = $1100 * 0.22 = $242
- Social Security tax withholding:
Total pay * Social security tax rate = $1100 * 0.062 = $68.20
- Medicare tax withholding:
Total pay * Medicare tax rate = $1100 * 0.0145 = $15.95
- Total withholding:
Federal income tax withholding + Social security tax withholding + Medicare tax withholding = $242 + $68.20 + $15.95 = $326.15
- Net pay:
Total pay – Total withholding = $1100 – $326.15 = $773.85
- Overtime tax:
Total withholding – Regular pay withholding = $326.15 – ($800 * 0.22) – ($800 * 0.062) – ($800 * 0.0145) = $314.29
As you can see, the overtime tax is simply the difference between the total withholding and the regular pay withholding in the U.S.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about overtime tax:
- The overtime pay rate is 1.5 times the regular pay rate for non-exempt employees.
- The federal income tax rate is the same for overtime pay as for regular pay.
- The Social Security and Medicare tax rates are also the same for overtime pay as for regular pay.
2. India
Indian labor laws dictate that overtime pay cannot exceed 1.5 times the regular pay rate.
For instance, if you’re an hourly employee in India with a standard rate of INR 200 per hour, your overtime rate of pay per hour would be calculated as follows:
Regular hourly rate x 1.5 = overtime rate of pay/hour
The equation goes as follows:
INR 200 x 1.5 = INR 300 overtime rate of pay/hour
Now, let’s assume you worked 5 additional hours that week. Your overtime pay would be calculated like this:
INR 300 overtime rate/hour x 5 overtime hours = INR 1,500 total overtime pay for that week
Once you know your overtime earnings, you can determine the tax implications.
For instance, if you fall into the 20% tax bracket and earn an additional INR 1,500 through overtime, your overtime tax would be calculated as follows:
Overtime pay x the income tax rate of 20% = overtime tax you owe
The equation goes as follows:
INR 1,500 x 20% (0.20) = INR 300 of overtime tax you owe
So, you would owe INR 300 in overtime tax for that specific period. This calculation is crucial for employees and employers in India who need to withhold the correct amount for taxes when processing payroll.
As we unravel the intricacies of calculating overtime and understanding its tax implications, it’s evident that accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
This is where Workstatus, the overtime tracker, seamlessly aligns with your needs.
Now, let’s delve into how Workstatus features can effortlessly transform how you handle overtime tracking.
1. Accurate Overtime Tracking For Overtime Calculations:
![]()
Workstatus is an overtime tracker tool that streamlines the intricacies of overtime tax calculations.
- Real-time Tracking
Workstatus, an extra work hour monitor, allows for real-time tracking, providing instant insights into ongoing work hours and aiding in proactive management of overtime and efficient resource allocation.
- Individual and Team Insights
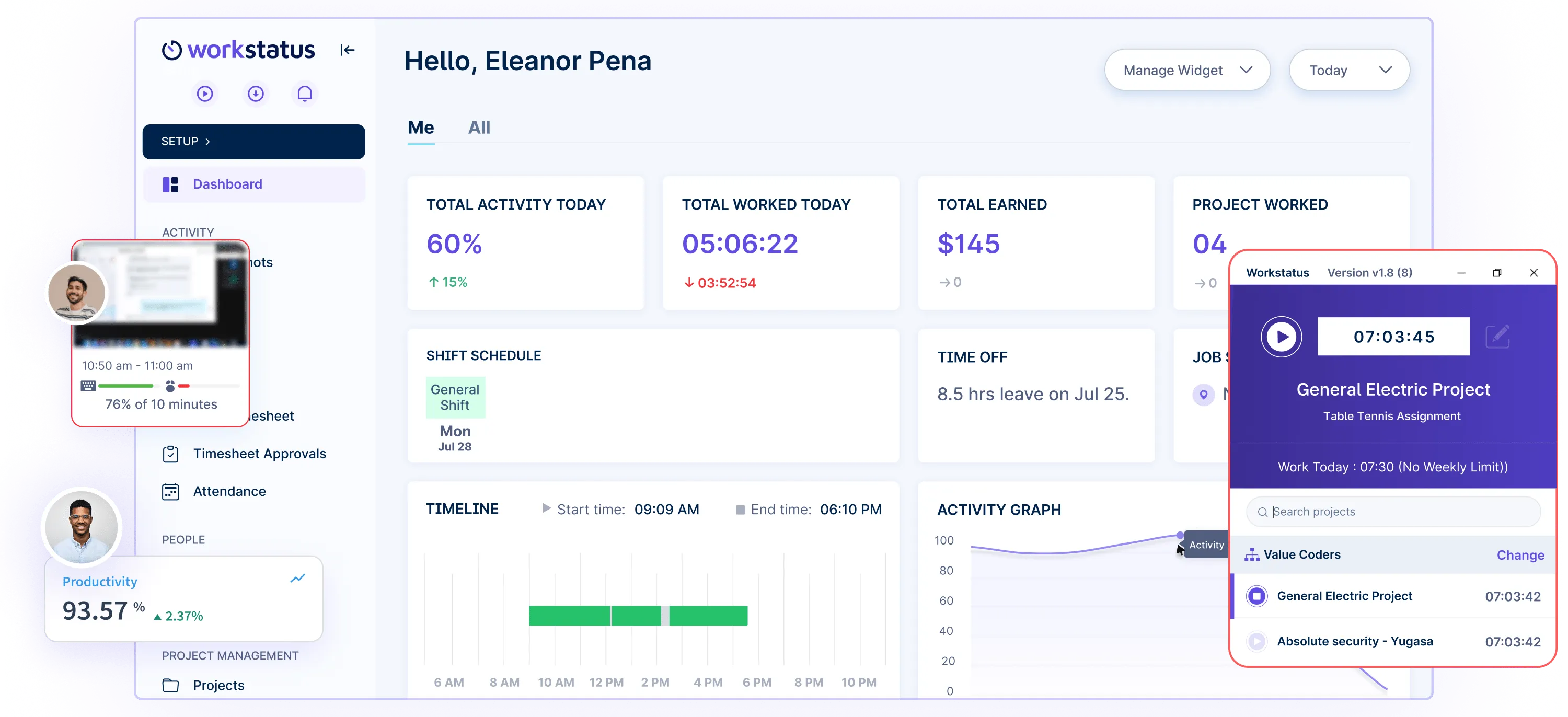
Workstatus captures individual and team-based overtime data, offering a holistic view of workforce productivity, enabling better project planning, and ensuring fair compensation.
2. Integration With Payroll Systems:
Workstatus’s seamless integration with payroll systems ensures a smooth process for overtime tax calculations.
- Error Reduction
The integration minimizes the risk of manual errors in payroll processing, guaranteeing accurate reflection of overtime pay in paychecks, reducing disputes, and fostering trust between employers and employees.
- Customizable Integration
Workstatus allows customizable integration with various payroll systems, accommodating the diverse structures of organizations and ensuring that overtime is accurately captured in the payroll cycle.
- Historical Data Access
The integrated payroll systems within Workstatus grant easy access to historical overtime data, facilitating trend analysis and budget planning and ensuring compliance with evolving overtime tax regulations.
3. Efficient Reporting For Overtime Taxation Compliance
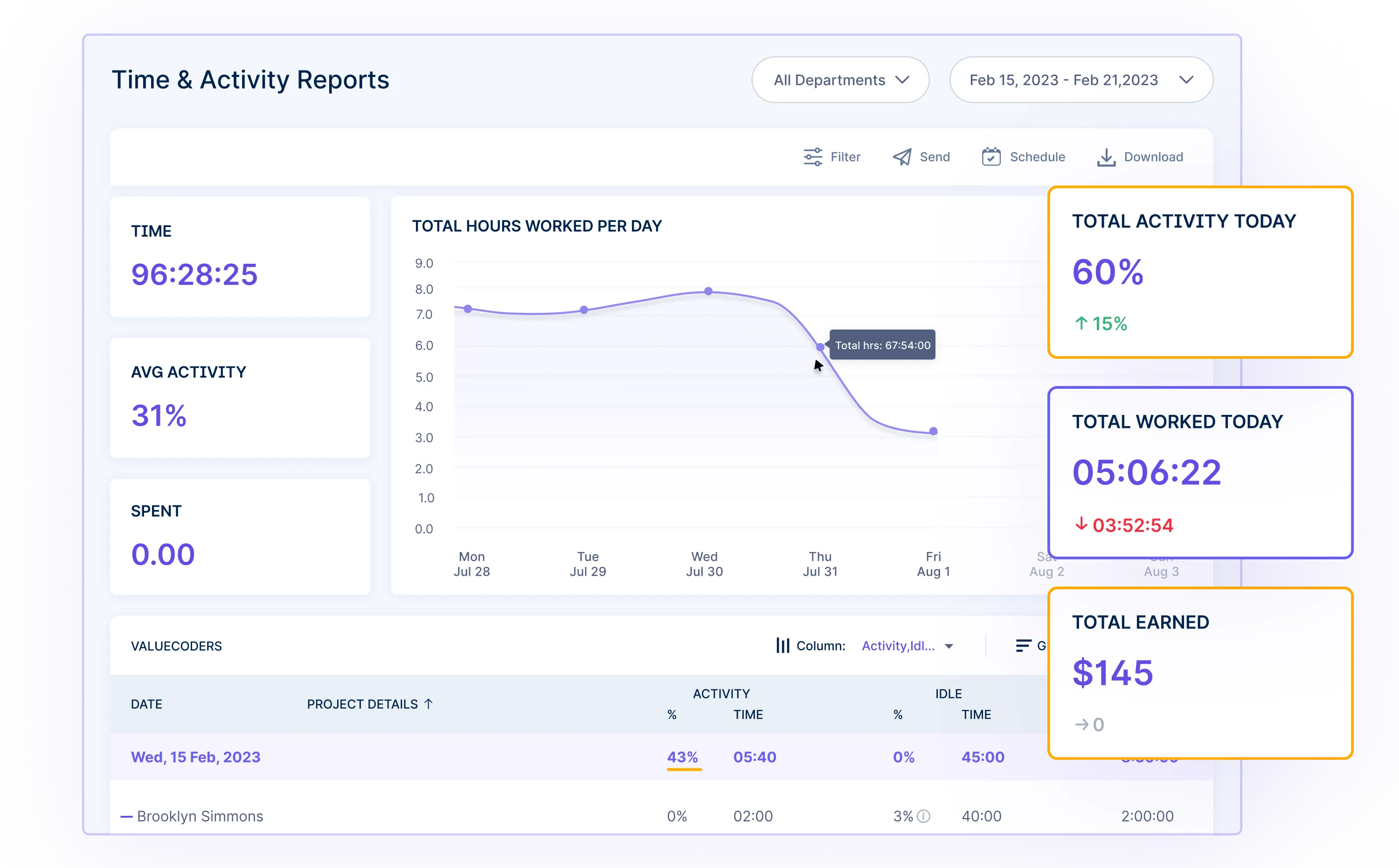
Workstatus’s reporting suite goes beyond compliance, offering insights into:
- Employee Productivity Reports
Identify top performers and areas for improvement, influencing overtime taxation considerations by recognizing efficient workers.
- Activity Reports
![]()
Track tasks to enhance efficiency, impacting overtime taxation planning by allocating hours judiciously.
- Project-related Reports
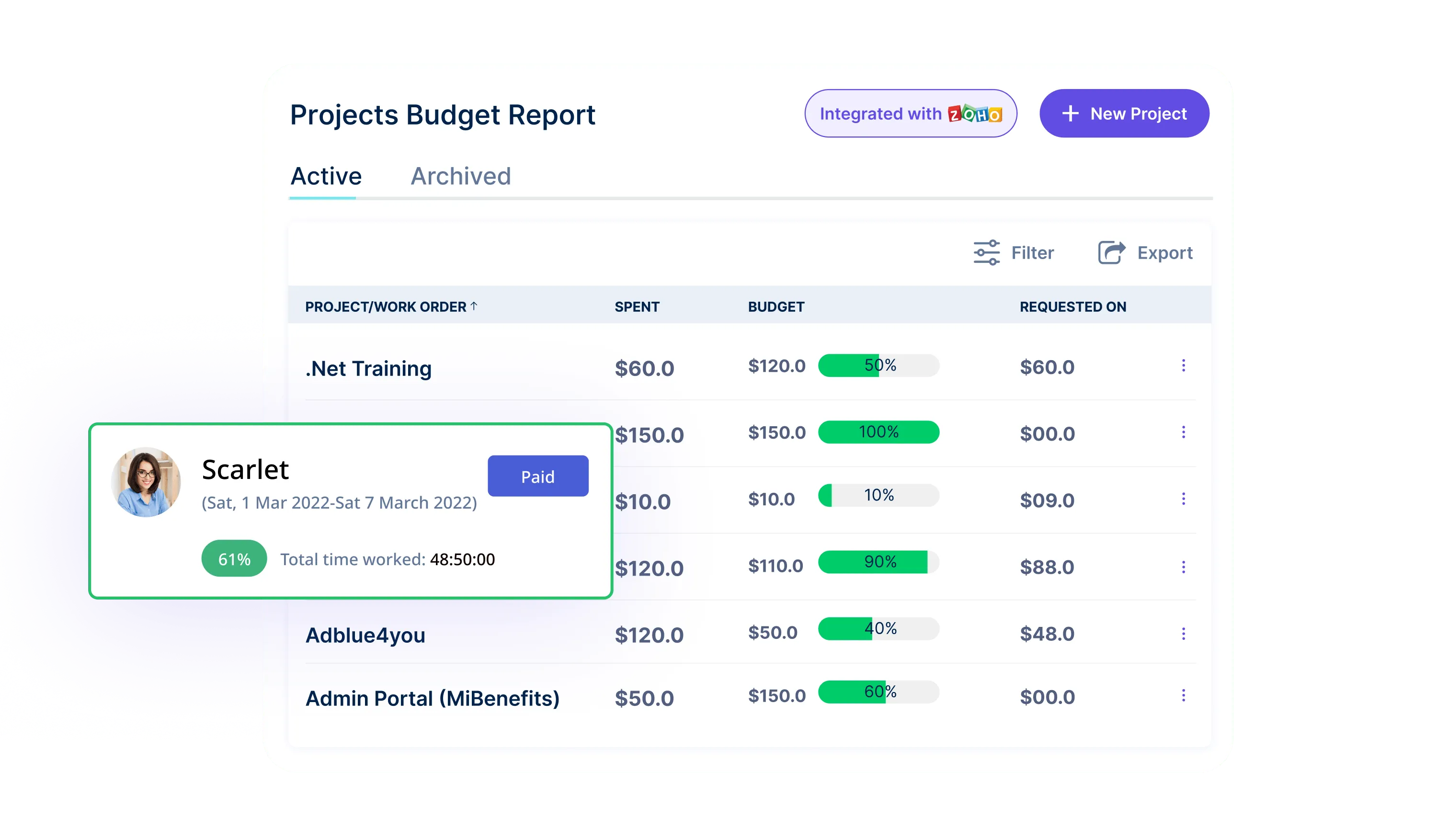
Monitor project timelines, aid project managers, and align overtime with critical project phases for strategic overtime taxation.
- Overtime Utilization Reports
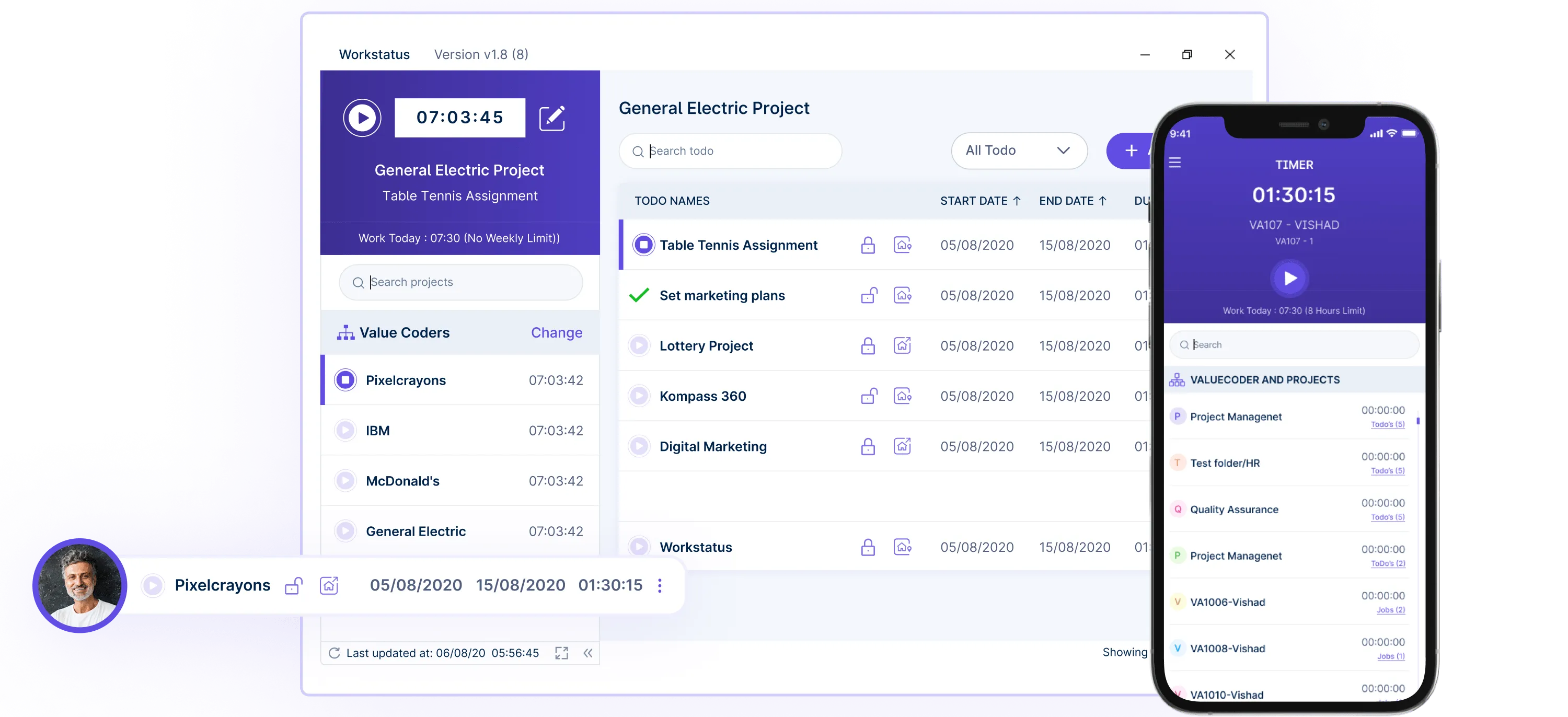
Track overtime allocation across tasks, optimizing productivity and ensuring compliance with overtime taxation rules.
- Time Management Reports
Evaluate time usage, guiding improvements, and strategic overtime taxation planning for efficient utilization.
4. Online Timesheets
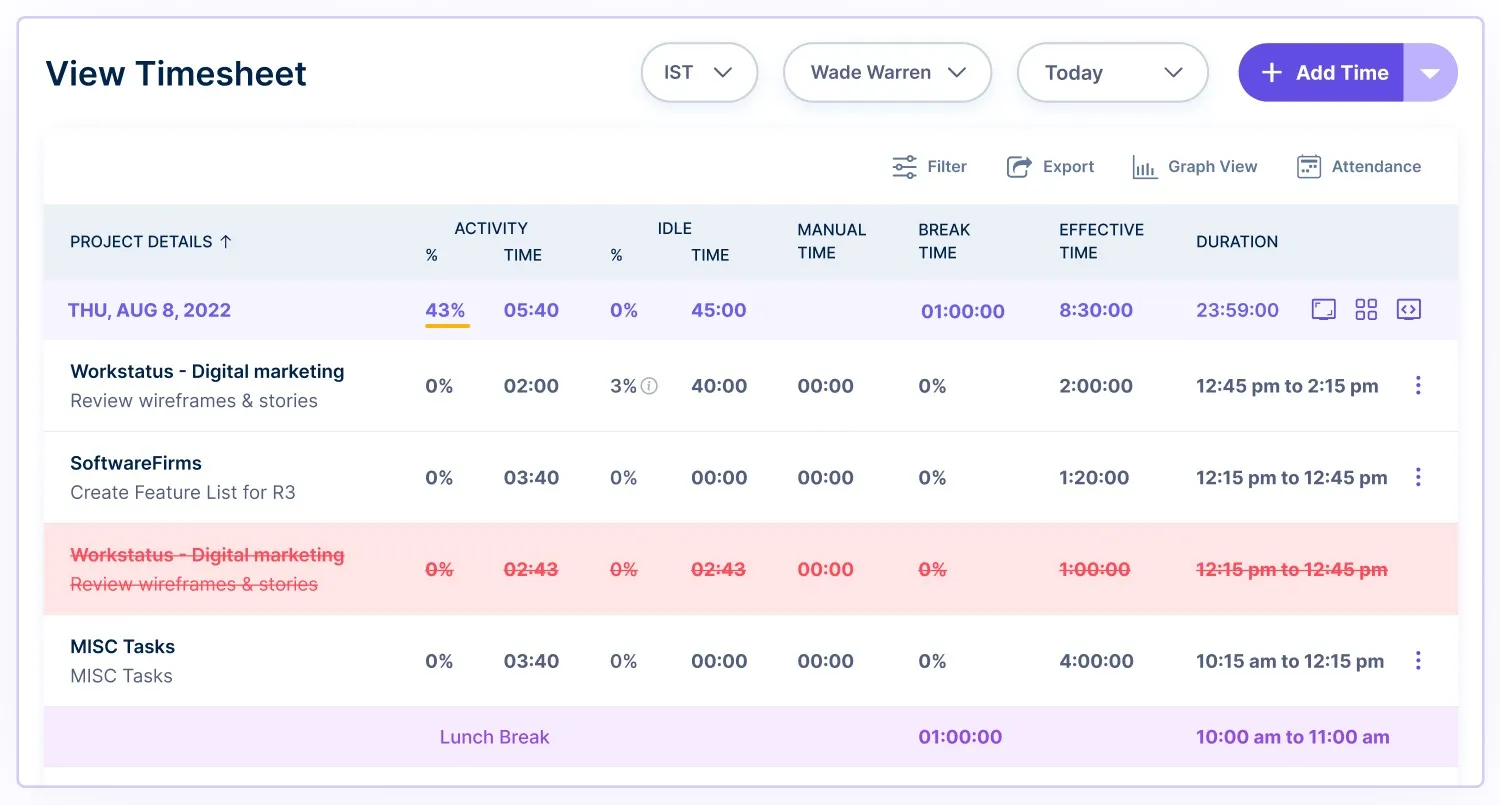
Workstatus’s Online Timesheets feature offers a comprehensive solution for tracking and managing overtime hours.
- Automated Overtime Calculation
Online timesheets automate overtime calculations based on recorded hours, eliminating the need for manual computations, reducing errors, and ensuring accurate overtime pay.
- Remote Accessibility
Employees can conveniently update their hours from any location, promoting flexibility in remote work scenarios and ensuring accurate overtime recording even when working offsite.
- Task-specific Time Allocation
Workstatus allows employees to allocate time to specific tasks or projects, providing a granular understanding of where overtime efforts are concentrated and aiding in project cost analysis.
5. Online Invoicing
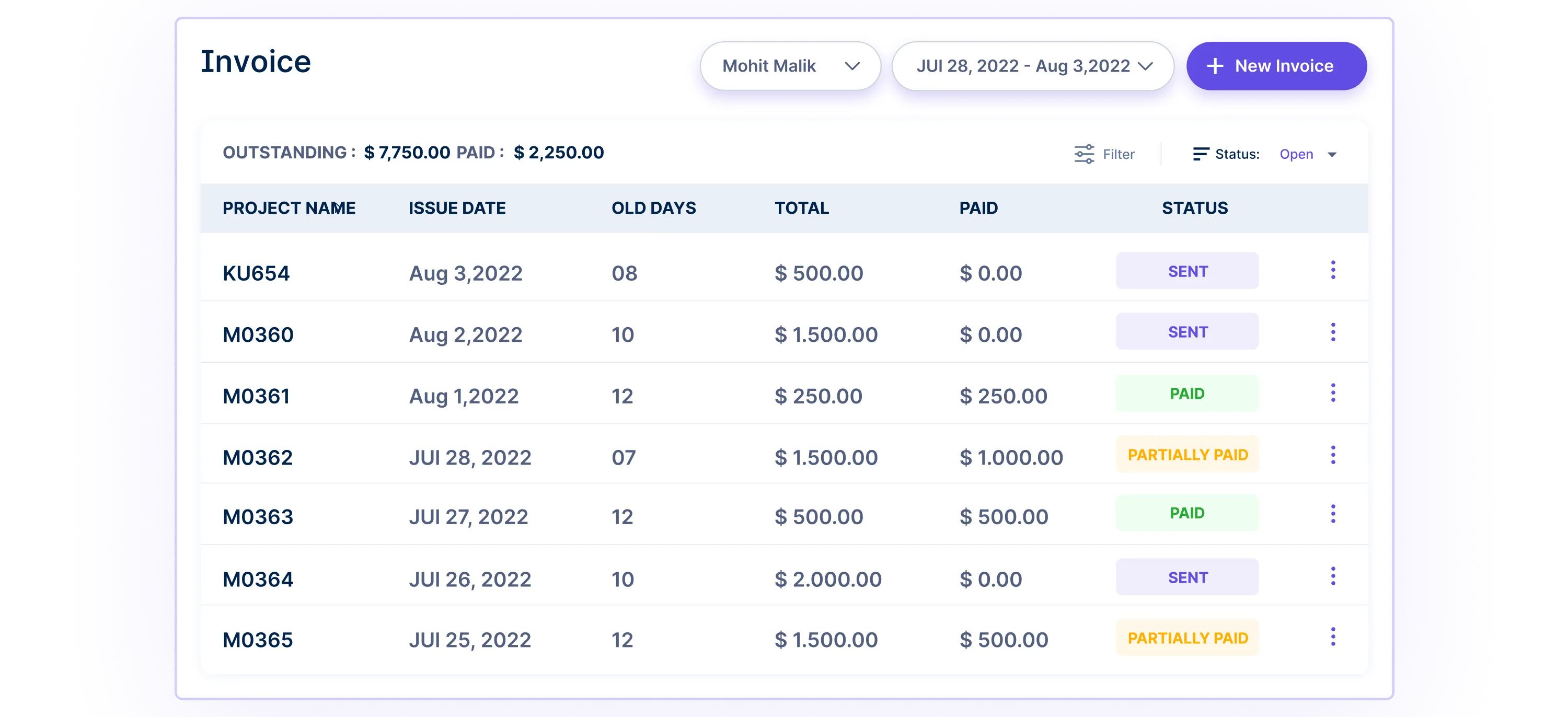
For freelancers and independent contractors relying on overtime for increased income, Workstatus’s Online Invoicing feature is a comprehensive tool.
- Detailed Hourly Billing
Online invoicing incorporates precise hourly details, making client billing transparent, reducing disputes, and ensuring fair compensation for overtime services.
- Time-Stamped Invoices
Invoices generated through Workstatus are time-stamped, providing a transparent and verifiable record of when the overtime work was performed, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Automated Invoice Generation
Overtime calculation software simplifies invoicing with automatic generation, reducing administrative burden and facilitating efficient financial management for freelancers and contractors.
Incorporating OT logging tools like Workstatus into your workflow simplifies overtime tax calculations.
It elevates accuracy, efficiency, and compliance with labor laws, fostering a seamless and transparent approach to workforce management.
Conclusion
In unraveling the intricacies of overtime taxation, we’ve empowered individuals and businesses with crucial insights.
Understanding the impact of overtime on taxes is not just about compliance but also about optimizing productivity and resource allocation.
Workstatus, the extra work hour monitor, emerges as a trusted ally in this journey, simplifying overtime tracking, aiding in accurate payroll integration, and providing insightful reports for strategic decision-making.
As you navigate the realm of overtime taxation, let Workstatus guide you toward efficiency, compliance, and a well-balanced approach to managing overtime.